|
Other articles:
|



 Nov 4, 2010 . Humans act toward people or things on the basis of the meanings they assign to those people or things.
Nov 4, 2010 . Humans act toward people or things on the basis of the meanings they assign to those people or things.
 Symbolic Interactionism, formulated by Blumer (1969) is the process of interaction in the formation of meanings for individuals. The inspiration for this .
Symbolic Interactionism as thought of by Herbert Blumer, is the process of interaction in the formation of meanings for individuals. Blumer was a devotee of .
Chicago School- The first school of symbolic interactionism that .
File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Quick View
File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Quick View
Symbolic Interactionism, formulated by Blumer (1969) is the process of interaction in the formation of meanings for individuals. The inspiration for this .
Symbolic Interactionism as thought of by Herbert Blumer, is the process of interaction in the formation of meanings for individuals. Blumer was a devotee of .
Chicago School- The first school of symbolic interactionism that .
File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Quick View
File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Quick View
 applying symbolic interationism to real life event . Hi! Thanks for taking the time to ask your question. First and foremost, here's a link that explains .
Symbolic Interactionism is based on three assumptions: . Game -- interaction where the child has the attitude of all the others involved in the game. .
The work succinctly and clearly developed a well-argued case for symbolic interaction as a perspective or theoretical framework to be judged by its capacity .
File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Quick View
faculty.chass.ncsu.edu/garson/PA765/symbolic.htm - SimilarFunctionalism, Systems Theory, Symbolic Interactionism, Social . Functionalism: -The sociological theory that ties to explain how a society is organized to perform functions effectively. This theory focuses on how the .
applying symbolic interationism to real life event . Hi! Thanks for taking the time to ask your question. First and foremost, here's a link that explains .
Symbolic Interactionism is based on three assumptions: . Game -- interaction where the child has the attitude of all the others involved in the game. .
The work succinctly and clearly developed a well-argued case for symbolic interaction as a perspective or theoretical framework to be judged by its capacity .
File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Quick View
faculty.chass.ncsu.edu/garson/PA765/symbolic.htm - SimilarFunctionalism, Systems Theory, Symbolic Interactionism, Social . Functionalism: -The sociological theory that ties to explain how a society is organized to perform functions effectively. This theory focuses on how the .
 The Society for the Study of Symbolic Interaction (SSSI) is an international professional organization of scholars interested in the study of a wide range .
The Society for the Study of Symbolic Interaction is a social science . As the main voice of the Symbolic Interactionist perspective, Symbolic Interaction .
The Society for the Study of Symbolic Interaction (SSSI) is an international professional organization of scholars interested in the study of a wide range .
The Society for the Study of Symbolic Interaction is a social science . As the main voice of the Symbolic Interactionist perspective, Symbolic Interaction .
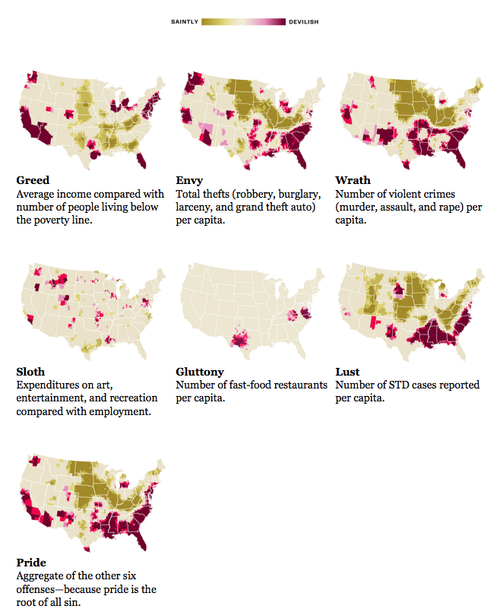 Symbolic Interactionism is Cool. by jose, Apr 29, 2009, at 07:58 pm. From Chris Orr at TNR's The Plank. Scientific proof that it is no longer possible to .
Jan 18, 2011 . "Following Mead, symbolic interactionists believe that the task of sociology is to study the ways in which interaction, and the symbols .
People find great meaning in symbols in their environment.
A theoretical school or orientation in sociological social psychology. An approach that has evolved principally from social behaviorism and the writings of .
There are 3 classic Sociological models of thought. (1) Functional(Durkheim/ Spencer)- belief that society is a system with different parts working as seperate units .
Symbolic Interactionism. “Symbols” are the basis of social life. Individuals and societies develop through people's interaction through symbols .
Feb 21, 2000 . Symbolic interactionism, or interactionism for short, is one of the major theoretical perspectives in sociology. This perspective has a long .
Symbolic Interactionism is Cool. by jose, Apr 29, 2009, at 07:58 pm. From Chris Orr at TNR's The Plank. Scientific proof that it is no longer possible to .
Jan 18, 2011 . "Following Mead, symbolic interactionists believe that the task of sociology is to study the ways in which interaction, and the symbols .
People find great meaning in symbols in their environment.
A theoretical school or orientation in sociological social psychology. An approach that has evolved principally from social behaviorism and the writings of .
There are 3 classic Sociological models of thought. (1) Functional(Durkheim/ Spencer)- belief that society is a system with different parts working as seperate units .
Symbolic Interactionism. “Symbols” are the basis of social life. Individuals and societies develop through people's interaction through symbols .
Feb 21, 2000 . Symbolic interactionism, or interactionism for short, is one of the major theoretical perspectives in sociology. This perspective has a long .
 Chemistry question: What kind of theory is Symbolic Interactionism? SYMBOLIC INTERACTIONISM IS 'SYMBOLIC' BECAUSE IT FOCUSES ON THE MEANINGS GIVEN TO .
File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Quick View
The methodological position of symbolic interactionism (SI) is "naturalistic". Science is a combination of exploration and inspection, which maps for SI .
Chemistry question: What kind of theory is Symbolic Interactionism? SYMBOLIC INTERACTIONISM IS 'SYMBOLIC' BECAUSE IT FOCUSES ON THE MEANINGS GIVEN TO .
File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Quick View
The methodological position of symbolic interactionism (SI) is "naturalistic". Science is a combination of exploration and inspection, which maps for SI .


 Mar 20, 2011 . What do Cuff, et. al. list as some of the basic principles of symbolic interactionism? To have symbolic interpretation, we need objects, .
Mar 20, 2011 . What do Cuff, et. al. list as some of the basic principles of symbolic interactionism? To have symbolic interpretation, we need objects, .
 department.monm.edu/portfolio/. /symbolic%20interactionism.pdf - SimilarSymbolic interactionism | Define Symbolic interactionism at . a theory that human interaction and communication is facilitated by words, gestures, and other symbols that have acquired conventionalized meanings. .
Jul 21, 2010 . Symbolic interactionism is a theory of sociology which frames individuals as social actors, and the self-society relationship is defined by .
File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Quick View
Symbolic interactionism is a sociological perspective on self and society based on the ideas of George H. Mead (1934), Charles H. Cooley (1902), .
Feb 3, 2000 . Symbolic Interactionism. Perhaps the most important and enduring sociological perspective from North America has been that of symbolic .
Symbolic interaction theory describes the family as a unit of interacting personalities. · This theory focuses attention on the way that people interact .
department.monm.edu/portfolio/. /symbolic%20interactionism.pdf - SimilarSymbolic interactionism | Define Symbolic interactionism at . a theory that human interaction and communication is facilitated by words, gestures, and other symbols that have acquired conventionalized meanings. .
Jul 21, 2010 . Symbolic interactionism is a theory of sociology which frames individuals as social actors, and the self-society relationship is defined by .
File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Quick View
Symbolic interactionism is a sociological perspective on self and society based on the ideas of George H. Mead (1934), Charles H. Cooley (1902), .
Feb 3, 2000 . Symbolic Interactionism. Perhaps the most important and enduring sociological perspective from North America has been that of symbolic .
Symbolic interaction theory describes the family as a unit of interacting personalities. · This theory focuses attention on the way that people interact .
 Symbolic interactionism is a major sociological perspective that places emphasis on micro-scale social interaction, which is particularly important in .
Symbolic interactionism is a major sociological perspective that places emphasis on micro-scale social interaction, which is particularly important in .
 Symbolic interactionism is a sociological perspective on self and society based on the ideas of George H. Mead (1934), Charles H. Cooley (1902), .
2 reviews - $19.83 - In stock
Page on the web site of leading UK SocioPsychologist Keith E Rice outlining the development and key concepts of Symbolic Ineractionism.
The graduate seminar SOC 5320 “Social Psychology: Symbolic Interactionism” integrates psychological, socio-psychological and sociological thought to .
Symbolic interactionism is a sociological perspective on self and society based on the ideas of George H. Mead (1934), Charles H. Cooley (1902), .
2 reviews - $19.83 - In stock
Page on the web site of leading UK SocioPsychologist Keith E Rice outlining the development and key concepts of Symbolic Ineractionism.
The graduate seminar SOC 5320 “Social Psychology: Symbolic Interactionism” integrates psychological, socio-psychological and sociological thought to .
 One proposition of symbolic interaction is that the greater a person's clarity of their role expectations, the greater the person's ability to perform that .
One proposition of symbolic interaction is that the greater a person's clarity of their role expectations, the greater the person's ability to perform that .
 Symbolic Interaction Theory summary with 16 pages of encyclopedia entries, . Get Symbolic Interactionism: Perspective and Method from Amazon.com .
Symbolic Interactionism: A student project at Iowa State University. Symbolic Interactionism As Defined By Herbert Blumer: (1996) A paper by C. Dodd Harris .
Symbolic Interaction Theory summary with 16 pages of encyclopedia entries, . Get Symbolic Interactionism: Perspective and Method from Amazon.com .
Symbolic Interactionism: A student project at Iowa State University. Symbolic Interactionism As Defined By Herbert Blumer: (1996) A paper by C. Dodd Harris .
 File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Quick View
Feb 8, 2011 . In symbolic interactionist thought, there is a difference between infrahuman and human society. In infrahuman life, cooperation is .
The book Symbolic Interaction and Cultural Studies, Edited by Howard S. Becker and Michal M. McCall is published by University of Chicago Press.
File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Quick View
Feb 8, 2011 . In symbolic interactionist thought, there is a difference between infrahuman and human society. In infrahuman life, cooperation is .
The book Symbolic Interaction and Cultural Studies, Edited by Howard S. Becker and Michal M. McCall is published by University of Chicago Press.
 File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Quick View
Since Mead regarded symbols as the foundation of both personal and social life, the theory he developed is called Symbolic Interactionism. .
File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Quick View
File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Quick View
Since Mead regarded symbols as the foundation of both personal and social life, the theory he developed is called Symbolic Interactionism. .
File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Quick View
 File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Quick View
by A Schneider - 1995 - Cited by 23 - Related articles
Symbolic interactionism is a social psychological theory developed from the work of Charles Horton Cooley and George Herbert Mead in the early part of the .
File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Quick View
by A Schneider - 1995 - Cited by 23 - Related articles
Symbolic interactionism is a social psychological theory developed from the work of Charles Horton Cooley and George Herbert Mead in the early part of the .
 Sitemap
Sitemap
|





































