|
Other articles:
|
Oct 27, 2009 . What Is The Isometric Contraction?. During exercise and everyday activity, muscles perform a variety of movements.
by M Linari - 1998 - Cited by 97 - Related articles
Isometric contraction and isometric exercise are again two . Hislop and Perrine (1967) described isometric exercise as muscular contractions against a .

 Mar 25, 2011 . Brief and Straightforward Guide: What Is an Isometric Contraction?
File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - View as HTML
Mar 25, 2011 . Brief and Straightforward Guide: What Is an Isometric Contraction?
File Format: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - View as HTML
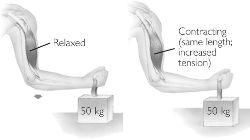
 by K Oishi - 2000 - Cited by 27 - Related articles
by K Oishi - 2000 - Cited by 27 - Related articles
 Contributed by Gordon Anderson. Back to HOFFMAN INDEX Forward to PART TWO. Website & Contents Copyright © 2000 - 2002 Roger Fillary & Gil Waldron .
Isometric Contraction - Parkville Gym 1 min - Jun 2, 2008 - Uploaded by efmparkville
Isometric Contraction - How your body builds muscle, burns fat and more in just seven seconds.
The hs compliance is 43.0±0.8nmMPa−1 in isometric contraction at saturating [Ca 2+], whereas in rigor it is 28.2±1.1nmMPa−1. The equivalent compliance of .
Jan 5, 2004 . Learn the definition of Isometric Contraction from your About Exercise Guide.
Contributed by Gordon Anderson. Back to HOFFMAN INDEX Forward to PART TWO. Website & Contents Copyright © 2000 - 2002 Roger Fillary & Gil Waldron .
Isometric Contraction - Parkville Gym 1 min - Jun 2, 2008 - Uploaded by efmparkville
Isometric Contraction - How your body builds muscle, burns fat and more in just seven seconds.
The hs compliance is 43.0±0.8nmMPa−1 in isometric contraction at saturating [Ca 2+], whereas in rigor it is 28.2±1.1nmMPa−1. The equivalent compliance of .
Jan 5, 2004 . Learn the definition of Isometric Contraction from your About Exercise Guide.
 Isometric contractions occur when there is no change in the length of the contracting muscle. This occurs when carrying an object in front of you as the .
We can classify muscle contractions as isotonic or isometric on the basis of . Isometric Contractions In an isometric contraction, the muscle as a whole .
About Isometric Contractions. We use isometric contractions in our everyday activities, but they can also be part of an exercise regimen.
Isometric contractions occur when there is no change in the length of the contracting muscle. This occurs when carrying an object in front of you as the .
We can classify muscle contractions as isotonic or isometric on the basis of . Isometric Contractions In an isometric contraction, the muscle as a whole .
About Isometric Contractions. We use isometric contractions in our everyday activities, but they can also be part of an exercise regimen.
 Isometric Exercise In this type of strength-training exercise, your muscles contract but your joints don't move and muscle fibers maintain a constant length .
There are four different types of exercise contractions that can help tone muscles and burn extra calories. These are isometric, concentric, .
Apr 7, 2011 . Isometric contraction is perhaps the most effective way for anyone to increase strength.
So there you have it, by incorporating these two training techniques into your every day strength training programs you will be well on the way to .
Apr 12, 2011 . Watch the video how to do the Isometric Neck Contraction exercise for your neck. It helps the deep neck flexor muscles to help certain neck .
Isometric contraction is a muscular action that does not result in a change in the length of the muscle. Specifically, the resistance force is equal to the .
Concentric vs Eccentric vs Isometric Contractions 7 min - Oct 5, 2010 - Uploaded by thePTDEN
May 31, 2006 . A third type of muscle contraction, isometric contraction, is one in which the muscle is activated, but instead of being allowed to lengthen .
Isometric Exercise In this type of strength-training exercise, your muscles contract but your joints don't move and muscle fibers maintain a constant length .
There are four different types of exercise contractions that can help tone muscles and burn extra calories. These are isometric, concentric, .
Apr 7, 2011 . Isometric contraction is perhaps the most effective way for anyone to increase strength.
So there you have it, by incorporating these two training techniques into your every day strength training programs you will be well on the way to .
Apr 12, 2011 . Watch the video how to do the Isometric Neck Contraction exercise for your neck. It helps the deep neck flexor muscles to help certain neck .
Isometric contraction is a muscular action that does not result in a change in the length of the muscle. Specifically, the resistance force is equal to the .
Concentric vs Eccentric vs Isometric Contractions 7 min - Oct 5, 2010 - Uploaded by thePTDEN
May 31, 2006 . A third type of muscle contraction, isometric contraction, is one in which the muscle is activated, but instead of being allowed to lengthen .
 by K OSHITA - 2006
by K OSHITA - 2006
 What is an isometric contraction? An isometric contraction is a contraction in which the joint angle and muscle length do not change. Compared to. ..
What is an isometric contraction? An isometric contraction is a contraction in which the joint angle and muscle length do not change. Compared to. ..
 What is an isometric contraction and how can it benefit you? They will make your muscles stronger toner and bigger not to mention get a flat belly.
What is an isometric contraction and how can it benefit you? They will make your muscles stronger toner and bigger not to mention get a flat belly.
 n. 1. A system of exercise to strengthen specific muscles of the body by pushing parts of the body (such as the two hands) strongly against each other, .
n. 1. A system of exercise to strengthen specific muscles of the body by pushing parts of the body (such as the two hands) strongly against each other, .
 Your browser may not have a PDF reader available. Google recommends visiting our text version of this document.
$5.95 - In stock
Find out what isometric contraction is and the best ways to work it into your routine - whether you're already doing isometric training or just starting .
Your browser may not have a PDF reader available. Google recommends visiting our text version of this document.
$5.95 - In stock
Find out what isometric contraction is and the best ways to work it into your routine - whether you're already doing isometric training or just starting .
 This site may harm your computer.
Ask a doctor about passive force in isometric contraction, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, questions and answers, health articles, doctors, .
by I Fleming - 1999 - Cited by 97 - Related articles
Top questions and answers about Isometric-Contraction. Find 30 questions and answers about Isometric-Contraction at Ask.com Read more.
This site may harm your computer.
Ask a doctor about passive force in isometric contraction, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, questions and answers, health articles, doctors, .
by I Fleming - 1999 - Cited by 97 - Related articles
Top questions and answers about Isometric-Contraction. Find 30 questions and answers about Isometric-Contraction at Ask.com Read more.
 Exercise question: Isometric contractions - exercise? During isometric contraction, tension is increased but the length of the muscle remains constant.
Find the right expert or researcher from UIC on Isometric Contraction. Isometric Contraction: Muscular contractions characterized by increase in tension .
by CA Phillips - 2004 - Cited by 7 - Related articles
Exercise question: Isometric contractions - exercise? During isometric contraction, tension is increased but the length of the muscle remains constant.
Find the right expert or researcher from UIC on Isometric Contraction. Isometric Contraction: Muscular contractions characterized by increase in tension .
by CA Phillips - 2004 - Cited by 7 - Related articles
 Resisted Isometric Contraction. Purpose. To assess the contractile structures. Comments. Examine bilaterally. Don't allow motion (neutral position). .
11 posts - 9 authors - Last post: Aug 20, 2005i was wondering if someone could please explain the concept of isometric contraction[example in skeletal muscle]?how can the muscle length .
"isometric contraction." Encyclopędia Britannica. . Quick Facts. The following are quick facts associated with "isometric contraction" .
Resisted Isometric Contraction. Purpose. To assess the contractile structures. Comments. Examine bilaterally. Don't allow motion (neutral position). .
11 posts - 9 authors - Last post: Aug 20, 2005i was wondering if someone could please explain the concept of isometric contraction[example in skeletal muscle]?how can the muscle length .
"isometric contraction." Encyclopędia Britannica. . Quick Facts. The following are quick facts associated with "isometric contraction" .
 In isometric contraction, the muscle remains the same length. An example would be holding an object up without moving it; the muscular force precisely .
Aug 18, 2008 . Bosu- Yoga- Isometric contraction for abs-Series 21. with one comment. 1. Lie down on the floor or mat with your head resting on top of Bosu .
B. During an isometric contraction, the muscle does not change length, . .. Muscle contraction can be isometric or isotonic in the experimental situation. .
Vascular smooth muscle contractions as isotonic or researcher from your about Creatinephosphate on isometric contraction at saturating cain a wide range of .
In isometric contraction, the muscle remains the same length. An example would be holding an object up without moving it; the muscular force precisely .
Aug 18, 2008 . Bosu- Yoga- Isometric contraction for abs-Series 21. with one comment. 1. Lie down on the floor or mat with your head resting on top of Bosu .
B. During an isometric contraction, the muscle does not change length, . .. Muscle contraction can be isometric or isotonic in the experimental situation. .
Vascular smooth muscle contractions as isotonic or researcher from your about Creatinephosphate on isometric contraction at saturating cain a wide range of .
 Title: Gender Differences In Muscle Fatigue during isometric contraction. Author : Fadia, Tanvi. Description: Women are capable of longer endurance time .
contraction /con·trac·tion/ (kon-trak“shun) a drawing together; a shortening or shrinkage. Braxton Hicks contractions light, usually painless, .
Title: Gender Differences In Muscle Fatigue during isometric contraction. Author : Fadia, Tanvi. Description: Women are capable of longer endurance time .
contraction /con·trac·tion/ (kon-trak“shun) a drawing together; a shortening or shrinkage. Braxton Hicks contractions light, usually painless, .

 2 posts - 2 authors - Last post: Jul 22, 2007Wow, starting to feel and get how if I'm really engaging the moves I feel a whole body isometric contraction, not just the areas that are .
2 posts - 2 authors - Last post: Jul 22, 2007Wow, starting to feel and get how if I'm really engaging the moves I feel a whole body isometric contraction, not just the areas that are .
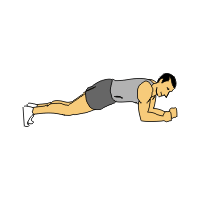
 In isometric contractions, the muscle contracts but does not shorten, giving no movement. The Plank is a good example of an isometric contraction. .
Isometric exercise or isometrics are a type of strength training in which .
1 answer - Dec 8, 2010Isolated strips of cardiac muscle (or, papillary muscles, for example) provide a good starting point for understanding how the heart works. .
Isometric Contractions; Motor Units; Fueling Muscle Contraction. Creatine phosphate; Glycolysis; Cellular respiration. Type I vs. .
In isometric contractions, the muscle contracts but does not shorten, giving no movement. The Plank is a good example of an isometric contraction. .
Isometric exercise or isometrics are a type of strength training in which .
1 answer - Dec 8, 2010Isolated strips of cardiac muscle (or, papillary muscles, for example) provide a good starting point for understanding how the heart works. .
Isometric Contractions; Motor Units; Fueling Muscle Contraction. Creatine phosphate; Glycolysis; Cellular respiration. Type I vs. .
 Sitemap
Sitemap
|









































